
The Simple API for XML APIs
The basic outline of the SAX parsing APIs are shown in Figure 4-1. To start the process, an instance of the
SAXParserFactoryclass is used to generate an instance of the parser.
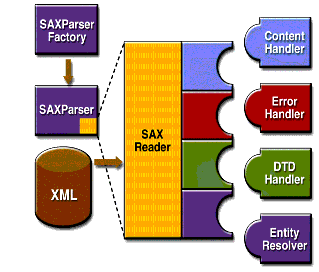
The parser wraps a
SAXReaderobject. When the parser'sparse()method is invoked, the reader invokes one of several callback methods implemented in the application. Those methods are defined by the interfacesContentHandler,ErrorHandler,DTDHandler, andEntityResolver.Here is a summary of the key SAX APIs:
SAXParserFactoryA
SAXParserFactoryobject creates an instance of the parser determined by the system property,javax.xml.parsers.SAXParserFactory.
SAXParserThe
SAXParserinterface defines several kinds ofparse()methods. In general, you pass an XML data source and aDefaultHandlerobject to the parser, which processes the XML and invokes the appropriate methods in the handler object.
SAXReaderThe
SAXParserwraps aSAXReader. Typically, you don't care about that, but every once in a while you need to get hold of it usingSAXParser'sgetXMLReader()so that you can configure it. It is theSAXReaderthat carries on the conversation with the SAX event handlers you define.
DefaultHandlerNot shown in the diagram, a
DefaultHandlerimplements theContentHandler,ErrorHandler,DTDHandler, andEntityResolverinterfaces (with null methods), so you can override only the ones you're interested in.
ContentHandlerMethods such as
startDocument,endDocument,startElement, andendElementare invoked when an XML tag is recognized. This interface also defines the methodscharactersandprocessingInstruction, which are invoked when the parser encounters the text in an XML element or an inline processing instruction, respectively.
ErrorHandlerMethods
error,fatalError, andwarningare invoked in response to various parsing errors. The default error handler throws an exception for fatal errors and ignores other errors (including validation errors). That's one reason you need to know something about the SAX parser, even if you are using the DOM. Sometimes, the application may be able to recover from a validation error. Other times, it may need to generate an exception. To ensure the correct handling, you'll need to supply your own error handler to the parser.
DTDHandlerDefines methods you will generally never be called upon to use. Used when processing a DTD to recognize and act on declarations for an unparsed entity.
EntityResolverThe
resolveEntitymethod is invoked when the parser must identify data identified by a URI. In most cases, a URI is simply a URL, which specifies the location of a document, but in some cases the document may be identified by a URN--a public identifier, or name, that is unique in the web space. The public identifier may be specified in addition to the URL. TheEntityResolvercan then use the public identifier instead of the URL to find the document--for example, to access a local copy of the document if one exists.A typical application implements most of the
ContentHandlermethods, at a minimum. Because the default implementations of the interfaces ignore all inputs except for fatal errors, a robust implementation may also want to implement theErrorHandlermethods.The SAX Packages
The SAX parser is defined in the packages listed in Table 4-1.