Creating the SwapRC Move
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
| IBM ILOG Scheduler User's Manual > Local Search in Scheduler > Tabu Search for the Jobshop Problem > Solving the Problem > Creating the SwapRC Move |
Creating the SwapRC Move |
INDEX
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
|
As described below, the N1 neighborhood consists of the swapping of all pairs of adjacent activities that are both on the same resource and on the same randomly selected critical path. In order to represent a single swap, we use the class SwapRC.
This class has two IloResourceConstraint data members, _rc and _after, which represent the original ordering before the swap takes place. That is, in the solution from which an instance of the SwapRC class is created, after is the next resource constraint of _rc. When a move has been performed, this order is reversed.
Aside from the standard accessor functions in the SwapRC class, there are three important methods: isReverseMove, createDelta, and findSwapFromDelta. Each of these functions are called by the N1 neighborhood class that we define below. Before describing where these methods are called, we describe each of them in turn.
The isReverseMove function accepts an IloSolution object that represents a move (a "delta" solution) and returns IloTrue if the delta represents a move that is the opposite of the current SwapRC instance. For example, given a SwapRC instance with _rc equal to resource constraint A and _after equal to resource constraint B, the move that it represents is a swap from A  B to B
B to B  A. Therefore, if the
A. Therefore, if the isReverseMove method of this instance is passed a delta where delta.getNextRC(A) is equal to B, the delta represents a move that reinserts the A  B relation. This is the reverse move and so the
B relation. This is the reverse move and so the isReverseMove methods returns IloTrue.
IloBool isReverseMove(IloSolution delta) const { IloSchedulerSolution schedDelta(delta); return (schedDelta.contains(_rc) && schedDelta.getNextRC(_rc).getImpl() == _after.getImpl()); } |
The second important method is createDelta. This function returns the IloSchedulerSolution object that represents the change to the current solution corresponding to the current SwapRC instance. The difference is simply to remove the next relation from _rc to _after and to insert the next relation from _after to _rc. The code of this function is more complex because other objects in the solution must be updated to be coherent with this swap. For example, if, in the current solution, resource constraint C is previous to _rc, we must update the next pointer of C to point to _after. Otherwise, we will be in a situation where _rc is next to both _after and C, obviously an infeasible state on a unary resource.
The steps in createDelta are the following. First, _rc and _after are added to the delta and their current next values are unset.
Then, if there is a resource constraint previous to _rc (like C in the example above), it is added to the delta and its next pointer is changed to be equal to _after.
Finally, the next of _after is set to _rc, and the next of _rc is set to what used to be the next of _after.
swapDelta.setNext(_after, _rc); // change _rc --> _after to _rc --> afterAfter if (current.hasNextRC(_after)) swapDelta.setNext(_rc, current.getNextRC(_after)); |
Figure 27.1 shows the next pointers for each resource constraint before and after the move is done. Note that all three pointers have changed, for example, the next of before is _rc before the move and is _after after the move.
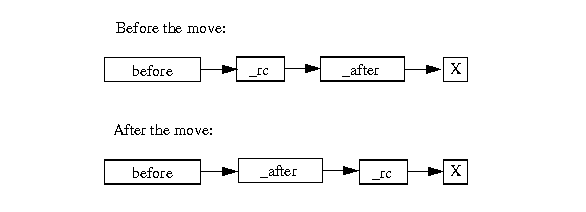
The resource constraints that do not change are not added to the delta. This ensures that they will be restored to their previous values by the local search protocol.
The final SwapRC method is findSwapFromDelta. This method, takes as input a delta solution and returns a corresponding SwapRC instance. This functionality is the inverse of createDelta: where createDelta returns a delta solution corresponding to a SwapRC instance, findSwapFromDelta returns a SwapRC instance corresponding to a delta solution.
| © Copyright IBM Corp. 1987, 2009. Legal terms. | PREVIOUS NEXT |