Complete Program and Output
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
| IBM ILOG Scheduler User's Manual > Advanced Concepts > Scheduling with Discrete Resources: the Ship-loading Problem > Complete Program and Output |
Complete Program and Output |
INDEX
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
|
You can see the entire program ship.cpp here or view it online in the standard distribution.
#include <ilsched/iloscheduler.h>
ILOSTLBEGIN
#if defined(ILO_SDXLOUTPUT)
#include "sdxloutput.h"
#endif
IloInt Capacity = 8;
IloInt NumberOfActivities = 34;
IloInt Durations [] = {3, 4, 4, 6, 5, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2,
3, 2, 1, 5, 2, 3, 2, 2, 1, 1,
1, 2, 4, 5, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 3,
2, 1, 2, 2 };
IloInt Demands [] = {4, 4, 3, 4, 5, 5, 4, 3, 4, 8,
4, 5, 4, 3, 3, 3, 6, 7, 4, 4,
4, 4, 7, 8, 8, 3, 3, 6, 8, 3,
3, 3, 3, 3 };
IloInt Precedences [] = {1, 2, 1, 4,
2, 3,
3, 5, 3, 7,
4, 5,
5, 6,
6, 8,
7, 8,
8, 9,
9, 10, 9, 14,
10, 11, 10, 12,
11, 13,
12, 13,
13, 15, 13, 16,
14, 15,
15, 18,
16, 17,
17, 18,
18, 19, 18, 20, 18, 21,
19, 23,
20, 23,
21, 22,
22, 23,
23, 24,
24, 25,
25, 26, 25, 30, 25, 31, 25, 32,
26, 27,
27, 28,
28, 29,
30, 28,
31, 28,
32, 33,
33, 34,
0, 0};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// PROBLEM DEFINITION
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void DefineProblem(IloModel model,
IloInt numberOfActivities,
IloInt* durations,
IloInt* demands,
IloInt capacity,
IloInt* precedences,
IloEnforcementLevel level,
IloNumVar& makespan)
{
IloEnv env = model.getEnv();
/* COMPUTE THE HORIZON. */
IloInt horizon = 0;
IloInt i;
for (i = 0; i < numberOfActivities; i++)
horizon += durations[i];
IloSchedulerEnv schedEnv (env);
schedEnv.setHorizon(horizon);
/* CREATE THE MAKESPAN VARIABLE. */
makespan = IloIntVar(env, 0, horizon);
/* CREATE THE RESOURCE. */
IloDiscreteResource resource(env, capacity);
resource.setCapacityEnforcement(level);
/* CREATE THE ACTIVITIES. */
IloArray<IloActivity> activities(env, numberOfActivities);
for (i = 0; i < numberOfActivities; i++) {
char name[128];
sprintf(name, "Activity %ld ", i+1);
activities[i] = IloActivity(env, durations[i], name);
model.add(activities[i].requires(resource, demands[i]));
model.add(activities[i].endsBefore(makespan));
}
/* POST THE PRECEDENCE CONSTRAINTS. */
IloInt precedenceIndex;
for (precedenceIndex = 0; ; precedenceIndex = precedenceIndex + 2) {
IloInt predNumber = precedences[precedenceIndex] - 1;
if (predNumber == -1)
break;
IloInt succNumber = precedences[precedenceIndex + 1] - 1;
model.add(activities[succNumber].startsAfterEnd(activities[predNumber]));
}
/* CLEAR THE ARRAY OF ACTIVITIES. */
activities.clear();
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// PRINTING OF SOLUTIONS
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void
PrintSolution(IlcScheduler scheduler)
{
for(IlcActivityIterator iterator(scheduler);
iterator.ok();
++iterator)
scheduler.getSolver().out() << *iterator << endl;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// MAIN FUNCTION
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
try {
IloEnv env;
IloEnforcementLevel level = IloBasic;
if (argc > 1) {
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "IloLow"))
level = IloLow;
else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "IloMediumLow"))
level = IloMediumLow;
else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "IloBasic"))
level = IloBasic;
else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "IloMediumHigh"))
level = IloMediumHigh;
else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "IloHigh"))
level = IloHigh;
else if (!strcmp(argv[1], "IloExtended"))
level = IloExtended;
}
IloModel model(env);
IloNumVar makespan;
DefineProblem(model,
NumberOfActivities,
Durations,
Demands,
Capacity,
Precedences,
level,
makespan);
model.add(IloMinimize(env, makespan));
// Algorithm
IloSolver solver(model);
IloGoal goal = IloSetTimesForward(env, makespan, IloSelFirstActMinEndMin);
if (solver.solve(goal)) {
PrintSolution(IlcScheduler(solver));
solver.printInformation();
#if defined(ILO_SDXLOUTPUT)
IloSDXLOutput output(env);
ofstream outFile("ship.xml");
output.write(IlcScheduler(solver), outFile, solver.getIntVar(makespan));
outFile.close();
#endif
}
else
solver.out() << "No solution!" << endl;
env.end();
} catch (IloException& exc) {
cout << exc << endl;
}
return 0;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// RESULTS
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/* ship IloBasic
Activity 34 [61 -- 2 --> 63]
Activity 33 [58 -- 2 --> 60]
Activity 32 [57 -- 1 --> 58]
Activity 31 [59 -- 2 --> 61]
Activity 30 [60 -- 3 --> 63]
Activity 29 [65 -- 1 --> 66]
Activity 28 [63 -- 2 --> 65]
Activity 27 [58 -- 1 --> 59]
Activity 26 [57 -- 1 --> 58]
Activity 25 [55 -- 2 --> 57]
Activity 24 [50 -- 5 --> 55]
Activity 23 [46 -- 4 --> 50]
Activity 22 [44 -- 2 --> 46]
Activity 21 [43 -- 1 --> 44]
Activity 20 [43 -- 1 --> 44]
Activity 19 [44 -- 1 --> 45]
Activity 18 [41 -- 2 --> 43]
Activity 17 [39 -- 2 --> 41]
Activity 16 [36 -- 3 --> 39]
Activity 15 [36 -- 2 --> 38]
Activity 14 [30 -- 5 --> 35]
Activity 13 [35 -- 1 --> 36]
Activity 12 [30 -- 2 --> 32]
Activity 11 [32 -- 3 --> 35]
Activity 10 [28 -- 2 --> 30]
Activity 9 [25 -- 3 --> 28]
Activity 8 [21 -- 4 --> 25]
Activity 7 [11 -- 3 --> 14]
Activity 6 [19 -- 2 --> 21]
Activity 5 [14 -- 5 --> 19]
Activity 4 [3 -- 6 --> 9]
Activity 3 [7 -- 4 --> 11]
Activity 2 [3 -- 4 --> 7]
Activity 1 [0 -- 3 --> 3]
*/
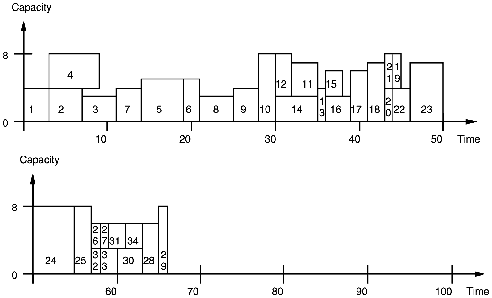
The results show the name of each activity followed by information about its place in the schedule. This information is enclosed in square brackets. It consists of three items: start time, duration, and end time of the activity.
For example, the results show that Activity 1 should begin on the first day (day 0), last three days, and terminate by day 3. The following diagram displays the solution, which is split in two parts (day 0 to day 50 and day 50 to day 66) simply for ease of viewing. The numbered blocks on that diagram represent the scheduled activities. Block 1, for example, begins on day 0 and ends by day 3. Block 2 begins on day 3 and ends by day 7.
In Chapter 18, we show how the ship-loading problem can be decomposed into several independent subproblems. A new program that exploits that feature is developed there.
| © Copyright IBM Corp. 1987, 2009. Legal terms. | PREVIOUS NEXT |