Complete Program and Output
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
| IBM ILOG Scheduler User's Manual > Advanced Concepts > Using Strong Propagation on Reservoirs: the Balance Constraint > Complete Program and Output |
Complete Program and Output |
INDEX
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
|
You can see the entire program balpos.cpp here or view it in the standard distribution.
#include <ilsched/iloscheduler.h>
ILOSTLBEGIN
IloInt NumberOfActivities = 15;
//---------------------------- PROBLEM 1 ------------------------------------
IloInt Durations01 [] = {
5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 14, 14, 14, 14, 15 };
IloInt NumberOfConstraints01 = 7;
IloInt Constraints01 [] = {
14, 15, 5,
4, 6, 24,
0, 3, 38,
1, 11, 117,
1, 8, 83,
4, 8, 50,
8, 14, 59 };
//---------------------------- PROBLEM 2 ------------------------------------
IloInt Durations02 [] = {
5, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 13, 14, 15 };
IloInt NumberOfConstraints02 = 7;
IloInt Constraints02 [] = {
3, 11, 88,
6, 8, 27,
1, 6, 48,
5, 8, 38,
9, 15, 55,
1, 3, 17,
1, 4, 27 };
//---------------------------- PROBLEM 3 ------------------------------------
IloInt Durations03 [] = {
5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8, 9, 9, 9, 10, 11, 14, 14, 15 };
IloInt NumberOfConstraints03 = 7;
IloInt Constraints03 [] = {
2, 3, 15,
5, 7, 17,
1, 7, 71,
2, 5, 44,
2, 6, 49,
2, 4, 29,
0, 3, 34 };
//----------------------- COMPUTE MAX MAKESPAN ----------------------------
IloNum getMakespanMax(const IloEnv& env,
IloInt numberOfActivities,
IloInt numberOfConstraints,
IloInt* durations,
IloInt* constraints) {
// THIS FUNCTION COMPUTES AN UPPER BOUND ON THE MAKESPAN BY ASSUMING
// ALL THE ACTIVITIES HAVE A DURATION EQUAL TO THE LONGEST ACTIVITY
// OF THE PROBLEM.
IloModel model(env);
IloNumVar makespan(env, 0, IloInfinity, ILOINT);
IloInt i, j, k, t;
// COMPUTE MAXIMAL DURATION OF ACTIVITIES
IloInt dmax = 0;
for (i=0; i < numberOfActivities; i++)
if (durations[i] > dmax)
dmax = durations[i];
IloActivity lact;
IloNumExprArray times(env, numberOfActivities+1);
for (i=0; i < numberOfActivities; i++) {
// USE ACTIVITIES WITH MAXIMAL DURATION
IloActivity act(env, dmax);
times[i] = act.getStartExpr();
if (i > 0)
model.add(act.startsAfterEnd(lact));
lact = act;
}
model.add(lact.endsBefore(makespan));
times[numberOfActivities] = makespan;
// ADD MINIMAL DELAY CONSTRAINTS
for (k=0; k < numberOfConstraints; k++) {
i = constraints[3*k];
j = constraints[(3*k) + 1];
t = constraints[(3*k) + 2];
model.add(times[j]-times[i] >= t);
}
// JUST PROPAGATE THE PERT
IloSolver solver(model);
IlcSearch s = solver.newSearch(IloGoalTrue(env));
s.next();
IloNum makespanMax = solver.getMin(makespan);
solver.end();
return makespanMax;
}
//----------------------------- MODEL -------------------------------------
IloModel
DefineModel(const IloEnv& env,
IloInt numberOfActivities,
IloInt numberOfConstraints,
IloInt* durations,
IloInt* constraints,
IloNumVar& makespan)
{
IloModel model(env);
IloUnaryResource ures(env);
// THIS ENFORCEMENT LEVEL WILL POST THE BALANCE CONSTRAINT
ures.setCapacityEnforcement(IloExtended);
// THIS ENFORCEMENT LEVEL WILL POST THE PRECEDENCE GRAPH CONSTRAINT
ures.setPrecedenceEnforcement(IloExtended);
IloReservoir reserv(env, 2, 0);
// THIS ENFORCEMENT LEVEL WILL POST THE BALANCE CONSTRAINT
reserv.setCapacityEnforcement(IloExtended);
// COMPUTES UPPER BOUND ON MAKESPAN
IloNum makespanMax = getMakespanMax(env,
numberOfActivities,
numberOfConstraints,
durations,
constraints);
makespan = IloNumVar(env, 0, makespanMax, ILOINT);
IloNumExprArray times(env, numberOfActivities + 1);
IloActivityArray acts(env, numberOfActivities);
// COMPUTE DURATION OF SHORTEST ACTIVITY
IloInt dmin = IloIntMax;
IloInt i, j, k, t;
for (i=0; i < numberOfActivities; i++)
if (durations[i] < dmin)
dmin = durations[i];
IloActivity lprod;
for (i=0; i < numberOfActivities; i++) {
acts[i]= IloActivity(env, durations[i]);
model.add(acts[i].requires(ures));
model.add(acts[i].requires(reserv, 1, IloAfterEnd));
model.add(acts[i].requires(reserv, 1, IloAfterStart));
model.add(acts[i].endsBefore(makespan));
IloActivity prod(env, 1);
model.add(prod.provides(reserv, 2, IloAfterStart));
times[i] = prod.getStartExpr();
if (i > 0)
// BUILD CHAIN OF PRODUCERS
model.add(prod.startsAfterStart(lprod, dmin));
lprod = prod;
}
times[numberOfActivities] = makespan;
model.add(times[numberOfActivities-1] + dmin <= makespan);
// BREAK EVIDENT SYMMETRIES BETWEEN ACTIVITIES WITH SAME DURATION
for (i=0; i < numberOfActivities - 1; i++)
for (j=i+1; j < numberOfActivities; j++)
if (durations[i] == durations[j]) {
model.add(acts[j].startsAfterEnd(acts[i]));
break;
}
// ADD DELAY CONSTRAINTS
for (k=0; k < numberOfConstraints; k++) {
i = constraints[3*k];
j = constraints[(3*k) + 1];
t = constraints[(3*k) + 2];
model.add(times[j]-times[i] >= t);
}
return model;
}
//-------------------------- DISPLAY SOLUTION -----------------------------
void
PrintSolution(const IloSolver& solver)
{
IlcScheduler sched(solver);
IlcUnaryResource res = *(IlcUnaryResourceIterator(sched));
for(IlcResourceConstraintIterator ite(res); ite.ok(); ++ite)
solver.out() << (*ite).getActivity() << endl;
}
//---------------------- INITIALIZE PARAMETERS -----------------------------
void
InitParameters(int argc,
char** argv,
IloInt& numberOfConstraints,
IloInt*& durations,
IloInt*& constraints)
{
IloInt p = 1;
if (argc > 1)
p = atol(argv[1]);
switch (p) {
case (1):
numberOfConstraints = NumberOfConstraints01;
durations = Durations01;
constraints = Constraints01;
break;
case (2):
numberOfConstraints = NumberOfConstraints02;
durations = Durations02;
constraints = Constraints02;
break;
case (3):
numberOfConstraints = NumberOfConstraints03;
durations = Durations03;
constraints = Constraints03;
break;
}
}
//------------------------- SOLVE PROBLEM ----------------------------------
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
try {
IloEnv env;
IloInt numberOfActivities = NumberOfActivities;
IloInt numberOfConstraints;
IloInt* durations;
IloInt* constraints;
InitParameters(argc, argv,
numberOfConstraints,
durations, constraints);
IloNumVar makespan;
IloModel model = DefineModel(env,
numberOfActivities,
numberOfConstraints,
durations,
constraints,
makespan);
model.add(IloMinimize(env, makespan));
IloSolver solver(model);
IlcSearch search = solver.newSearch(IloRankForward(env, makespan));
IloInt sumd = 0;
for (IloInt i=0; i < numberOfActivities; i++)
sumd += durations[i];
while (search.next()) {
solver.out() << "SOLUTION WITH SLACK = "
<< solver.getIntVar(makespan).getMin() - sumd << endl;
PrintSolution(solver);
}
solver.printInformation();
solver.end();
env.end();
} catch (IloException& exc) {
cout << exc << endl;
}
return 0;
}
An optimal solution for the first problem is described in Figure 22.4. It corresponds to a slack duration of 22 (5 between t0 and t1, 2 between t5 and t6, 6 between t7 and t8, 8 between t10 and t11 and 1 between t13 and t14) for an optimal makespan of 157.
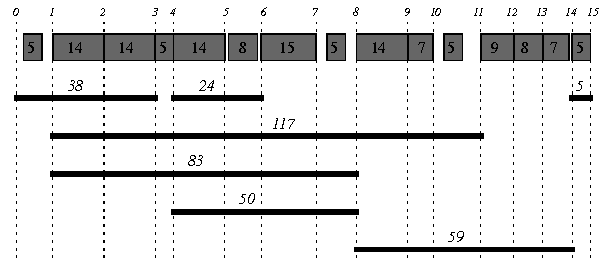
This optimal solution is quickly found after 2 iterations and 28 backtracks.
| © Copyright IBM Corp. 1987, 2009. Legal terms. | PREVIOUS NEXT |