Experimental details

|
Experimental details |

|
|
Mobility & Peer Estimator is the MAC component which
About gathering IEEE 802.11 raw RSSI data, due to the relative novelty and high heterogeneity of wireless technologies, there is currently no standard specification, widely accepted by vendors and available in most common operating systems, of an application-level API to achieve full RSSI visibility. For this reason, we have developed our own portable 80211NetworkInterface component which includes different implementations of RSSI monitoring mechanisms, which are automatically selected depending on the specific characteristics of served client devices. To achieve maximum portability, MobilityEstimator exploits 80211NetworkInterface component. In particular, it provides an original and operating-system-transparent Java API to obtain the list of all APs in current visibility and their related RSSI information. For Linux clients, it gathers those monitoring data via the standardized API provided by the Linux Wireless Extensions. For Windows CE/.NET clients, instead, it transparently binds the same Java API to the monitoring functionality provided by the Microsoft Network Driver Interface Specification User-mode I/O (NDISUIO), which is platform-dependent but portable among different wireless interface implementations. For instance, it exploits the NDISUIO function DeviceIOControl() to query the OID_802_11_BSSID_LIST_SCAN object to retrieve the complete list of currently reachable IEEE 802.11 APs. Moreover, 80211NetworkInterface component is able to interact with our original IEEE 802.11 simulator to make possible, mainly for experimental purposes, the exploitation of MobilityEstimator even if it is not available any actual IEEE 802.11 environment. 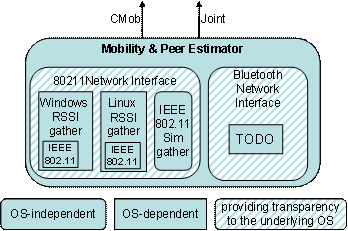 Mobility and Peer Estimator In the future we want to validate our MPE prototype in wireless scenarios with different AP distributions, different area dimensions, great signal noise. The main objective is to achieve upper and lower bounds for the Still/Motion states, checling their validity in several heterogeneous wireless scenarios. Novel information will be published as soon as possible. |
||
| 9-nov-09 |